From State to Edges: How LangGraph Connects the Dots
by Adithya Hebbar, System Analyst
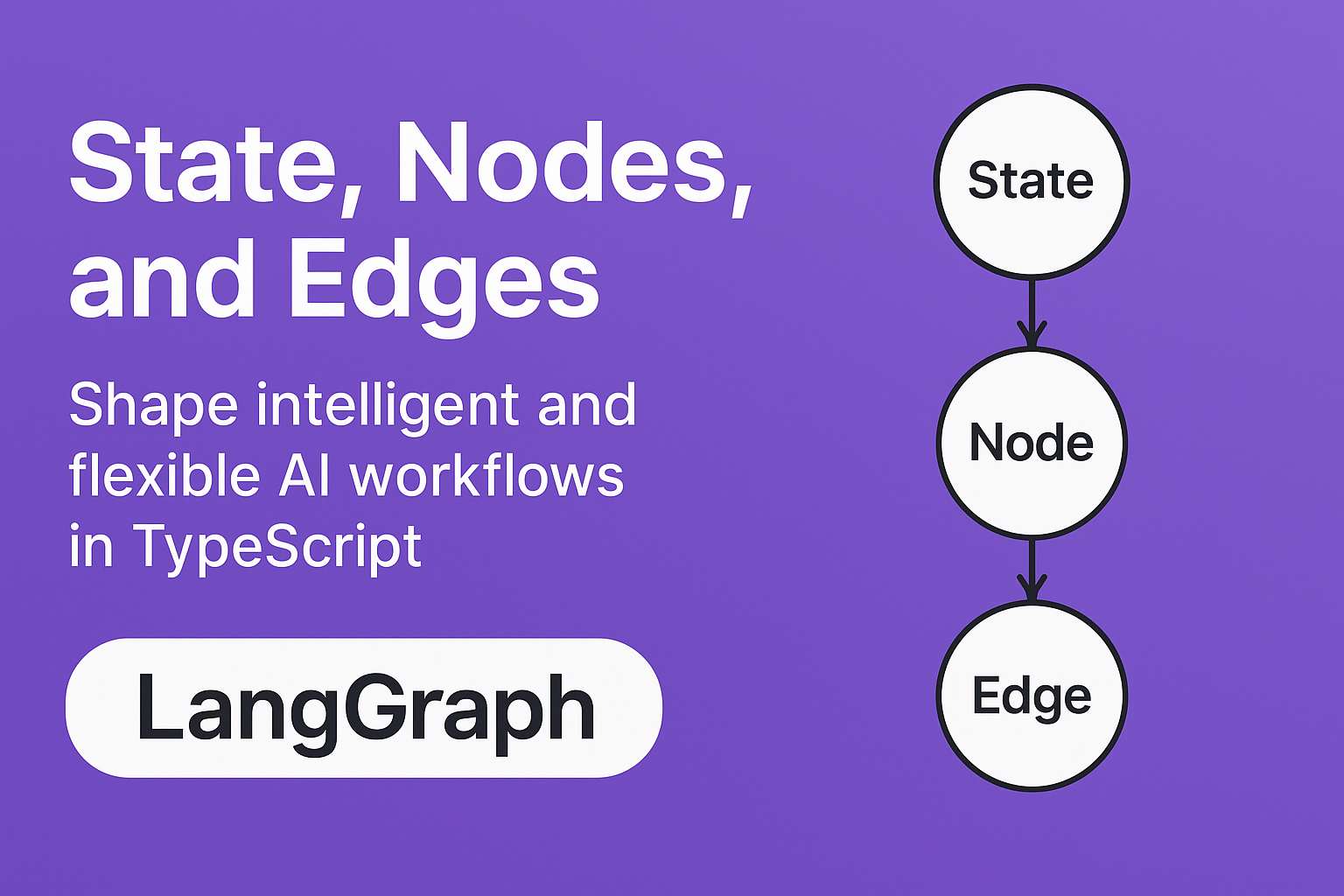
In LangGraph, everything revolves around three core concepts: States, Nodes, and Edges. Understanding how these work together is key to building effective AI workflows.
States: Your Data Container
States are like containers that hold all the information your workflow needs. They define what data is available and how it gets updated.
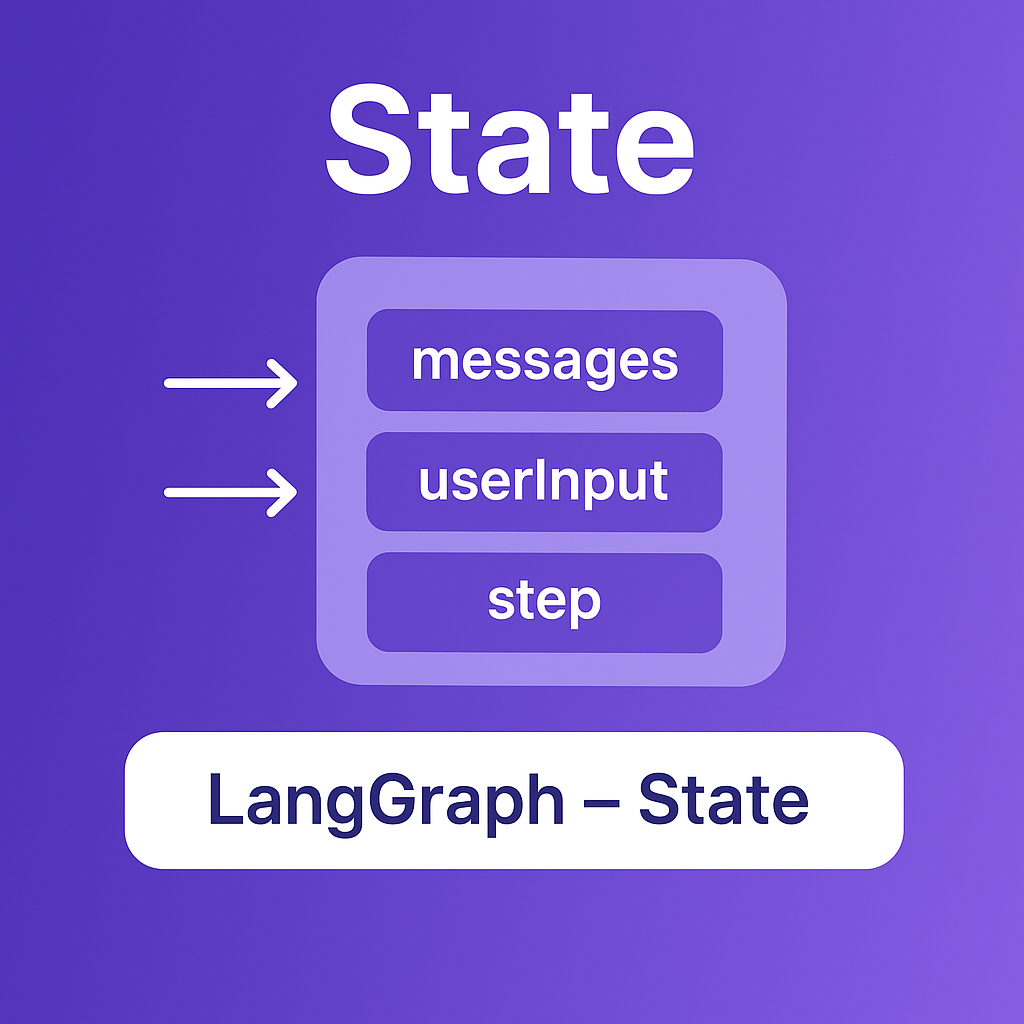
Simple State Example
Let's start with a basic state that holds a conversation:
import { Annotation } from '@langchain/langgraph';
import { BaseMessage } from '@langchain/core/messages';
// Define what our state looks like
const State = Annotation.Root({
messages: Annotation<BaseMessage[]>({
reducer: (existing, newMessages) => existing.concat(newMessages),
default: () => [],
}),
userInput: Annotation<string>({
reducer: (x, y) => y ?? x,
default: () => '',
}),
step: Annotation<string>({
reducer: (x, y) => y ?? x,
default: () => 'start',
}),
});The reducer function tells LangGraph how to combine new data with existing data. For messages, we append new ones to the list. For simple values like userInput and step, we just replace the old value with the new one.
Nodes: Your Processing Functions
Nodes are functions that take the current state, do something with it, and return updates to the state.
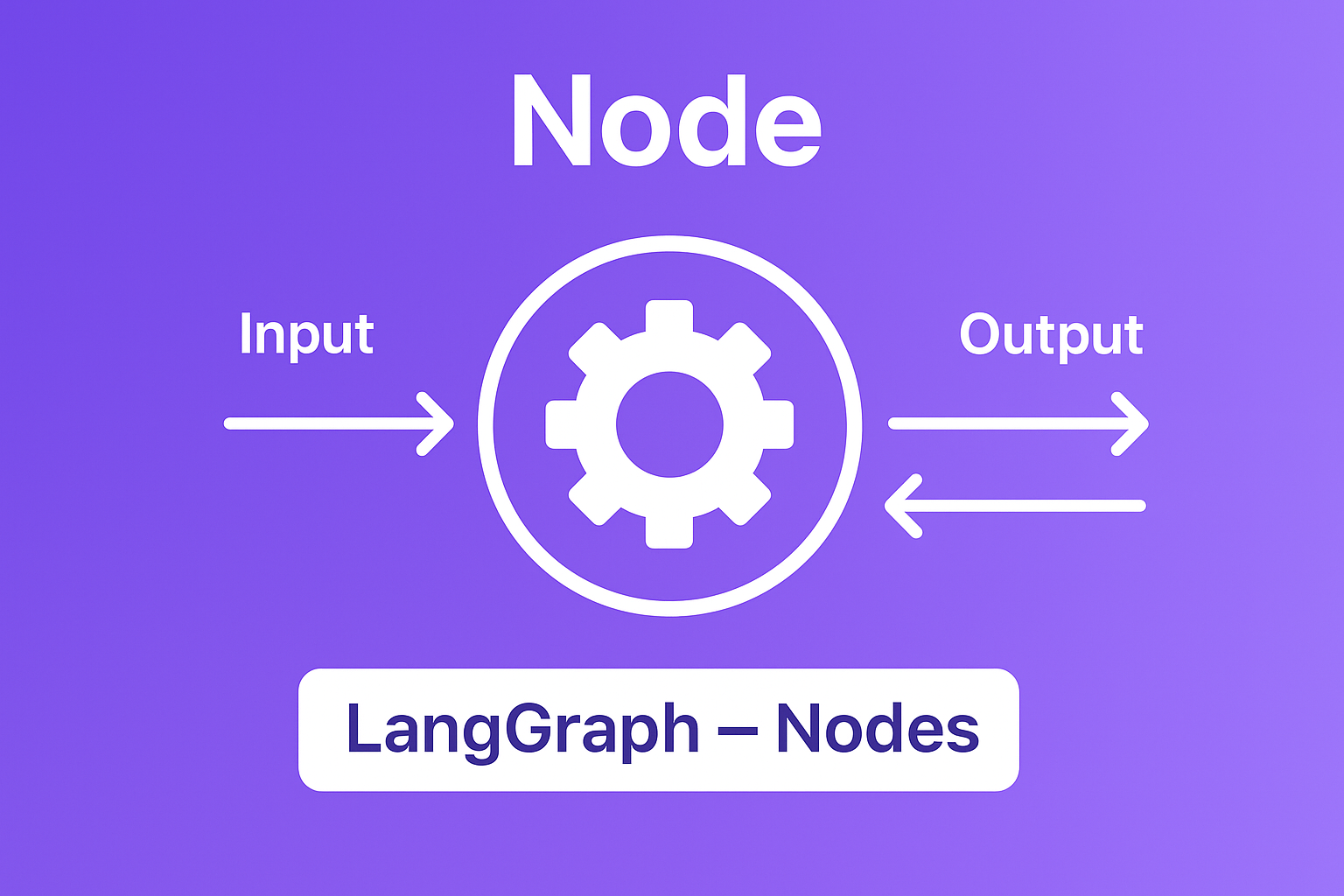
Basic Node Example
Here's a simple node that processes user input:
import { HumanMessage, AIMessage } from '@langchain/core/messages';
import { ChatOpenAI } from '@langchain/openai';
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
modelName: 'gpt-4o',
temperature: 0.7,
});
async function processInput(state: typeof State.State) {
const { userInput, messages } = state;
// Add the user's message to our conversation
const userMessage = new HumanMessage(userInput);
const allMessages = [...messages, userMessage];
// Get a response from the AI
const response = await model.invoke(allMessages);
// Return updates to the state
return {
messages: [response], // Add the AI's response
step: 'processed', // Update our step
};
}Edges: Your Decision Logic
Edges decide which node to run next based on the current state. They're like the arrows in a flowchart.
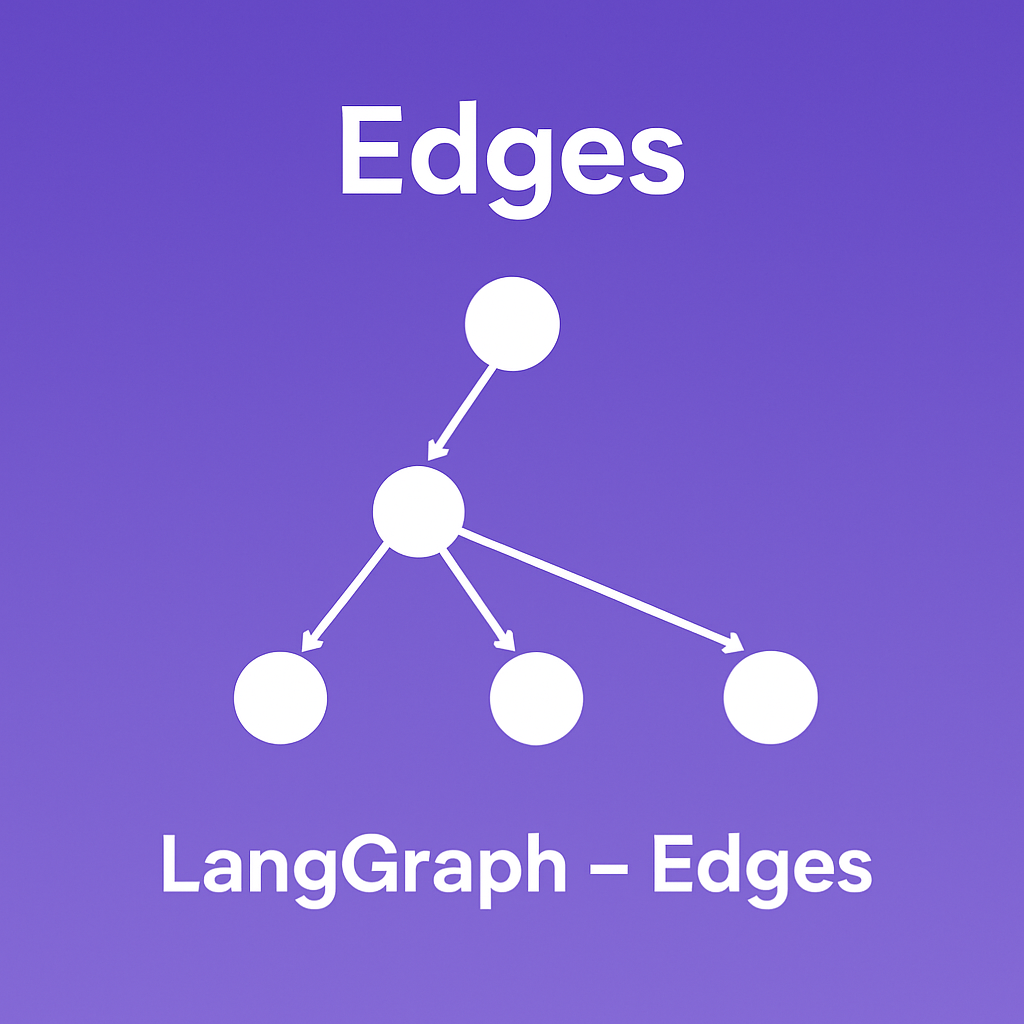
Simple Edge Function
import { END } from '@langchain/langgraph';
function decideNext(state: typeof State.State) {
const { step } = state;
if (step === 'start') {
return 'processInput';
} else if (step === 'processed') {
return 'checkComplete';
} else if (step === 'complete') {
return END; // Stop the workflow
} else {
return 'processInput'; // Default: keep processing
}
}Example: AI-Powered Customer Support Bot
Here's a practical example that uses AI for intelligent message categorization and routing:
import { Annotation, StateGraph, START, END } from '@langchain/langgraph';
import { ChatOpenAI } from '@langchain/openai';
import { HumanMessage, SystemMessage } from '@langchain/core/messages';
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
modelName: 'gpt-4o',
temperature: 0.1, // Low temperature for consistent categorization
});
// State for customer support
const SupportState = Annotation.Root({
userMessage: Annotation<string>({
reducer: (x, y) => y ?? x,
default: () => '',
}),
category: Annotation<string>({
reducer: (x, y) => y ?? x,
default: () => '',
}),
response: Annotation<string>({
reducer: (x, y) => y ?? x,
default: () => '',
}),
step: Annotation<string>({
reducer: (x, y) => y ?? x,
default: () => 'start',
}),
});
// AI-powered categorization node
async function categorizeMessage(state: typeof SupportState.State) {
const { userMessage } = state;
const systemPrompt = `You are a customer support categorization AI.
Analyze the user's message and categorize it into one of these categories:
- billing: Payment issues, subscription problems, billing questions
- technical: App bugs, technical problems, feature issues
- refunds: Return requests, refund inquiries, cancellation issues
- general: Greetings, general questions, unclear requests
Respond with ONLY the category name, nothing else.`;
const messages = [
new SystemMessage(systemPrompt),
new HumanMessage(userMessage),
];
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
const category = response.content.toString().toLowerCase().trim();
return {
category,
step: 'categorized',
};
}
// AI-powered response handlers
async function handleBilling(state: typeof SupportState.State) {
const { userMessage } = state;
const systemPrompt = `You are a billing support specialist.
Help the customer with their billing-related issue. Be helpful and professional.
If you need to escalate, mention that you'll connect them with a billing specialist.`;
const messages = [
new SystemMessage(systemPrompt),
new HumanMessage(userMessage),
];
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
return {
response: response.content.toString(),
step: 'completed',
};
}
async function handleTechnical(state: typeof SupportState.State) {
const { userMessage } = state;
const systemPrompt = `You are a technical support specialist.
Help the customer with their technical issue. Provide troubleshooting steps when possible.
If the issue is complex, mention that you'll connect them with a technical specialist.`;
const messages = [
new SystemMessage(systemPrompt),
new HumanMessage(userMessage),
];
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
return {
response: response.content.toString(),
step: 'completed',
};
}
async function handleRefunds(state: typeof SupportState.State) {
const { userMessage } = state;
const systemPrompt = `You are a refunds specialist.
Help the customer with their refund or return request. Be empathetic and clear about the process.
Mention that the refunds team will review their request within 24 hours.`;
const messages = [
new SystemMessage(systemPrompt),
new HumanMessage(userMessage),
];
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
return {
response: response.content.toString(),
step: 'completed',
};
}
async function handleGeneral(state: typeof SupportState.State) {
const { userMessage } = state;
const systemPrompt = `You are a general customer support agent.
Help the customer with their inquiry. Be friendly and ask clarifying questions if needed.
If you can't help directly, offer to connect them with the appropriate specialist.`;
const messages = [
new SystemMessage(systemPrompt),
new HumanMessage(userMessage),
];
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
return {
response: response.content.toString(),
step: 'completed',
};
}
// Edge logic
function routeByCategory(state: typeof SupportState.State) {
const { category } = state;
switch (category) {
case 'billing':
return 'handleBilling';
case 'technical':
return 'handleTechnical';
case 'refunds':
return 'handleRefunds';
default:
return 'handleGeneral';
}
}
// Build the graph
const workflow = new StateGraph(SupportState)
.addNode('categorizeMessage', categorizeMessage)
.addNode('handleBilling', handleBilling)
.addNode('handleTechnical', handleTechnical)
.addNode('handleRefunds', handleRefunds)
.addNode('handleGeneral', handleGeneral)
.addEdge(START, 'categorizeMessage')
.addConditionalEdges('categorizeMessage', routeByCategory, {
handleBilling: 'handleBilling',
handleTechnical: 'handleTechnical',
handleRefunds: 'handleRefunds',
handleGeneral: 'handleGeneral',
})
.addEdge('handleBilling', END)
.addEdge('handleTechnical', END)
.addEdge('handleRefunds', END)
.addEdge('handleGeneral', END);
export const graph = workflow.compile();Understanding the Three Pillars
States: The Foundation
- Define what data your workflow needs
- Use reducers to control how data gets merged
- Keep your state structure simple and focused
Nodes: The Workers
- Each node should have a single responsibility
- Always return updates to the state
- Handle errors gracefully within nodes
Edges: The Decision Makers
- Use edges to create branching logic
- Make decisions based on state values
- Keep edge functions simple and predictable
Best Practices
- Start Simple: Begin with basic states and add complexity gradually
- Single Responsibility: Each node should do one thing well
- Clear Logic: Make your edge conditions easy to understand
- Test Thoroughly: Try different inputs to ensure your workflow handles all scenarios
Mastering these three concepts will give you the foundation to build sophisticated AI workflows with LangGraph.